The Mickey Mouse–shaped solar array near Epcot is made of 48,000 solar panels and is operated by Duke Energy. (Photo: Duke Energy)
There is extra significance to the American Nuclear Society holding its annual meeting in Orlando, Florida, this past week. That’s because in 1967, the state of Florida passed a law allowing Disney World to build a nuclear power plant.
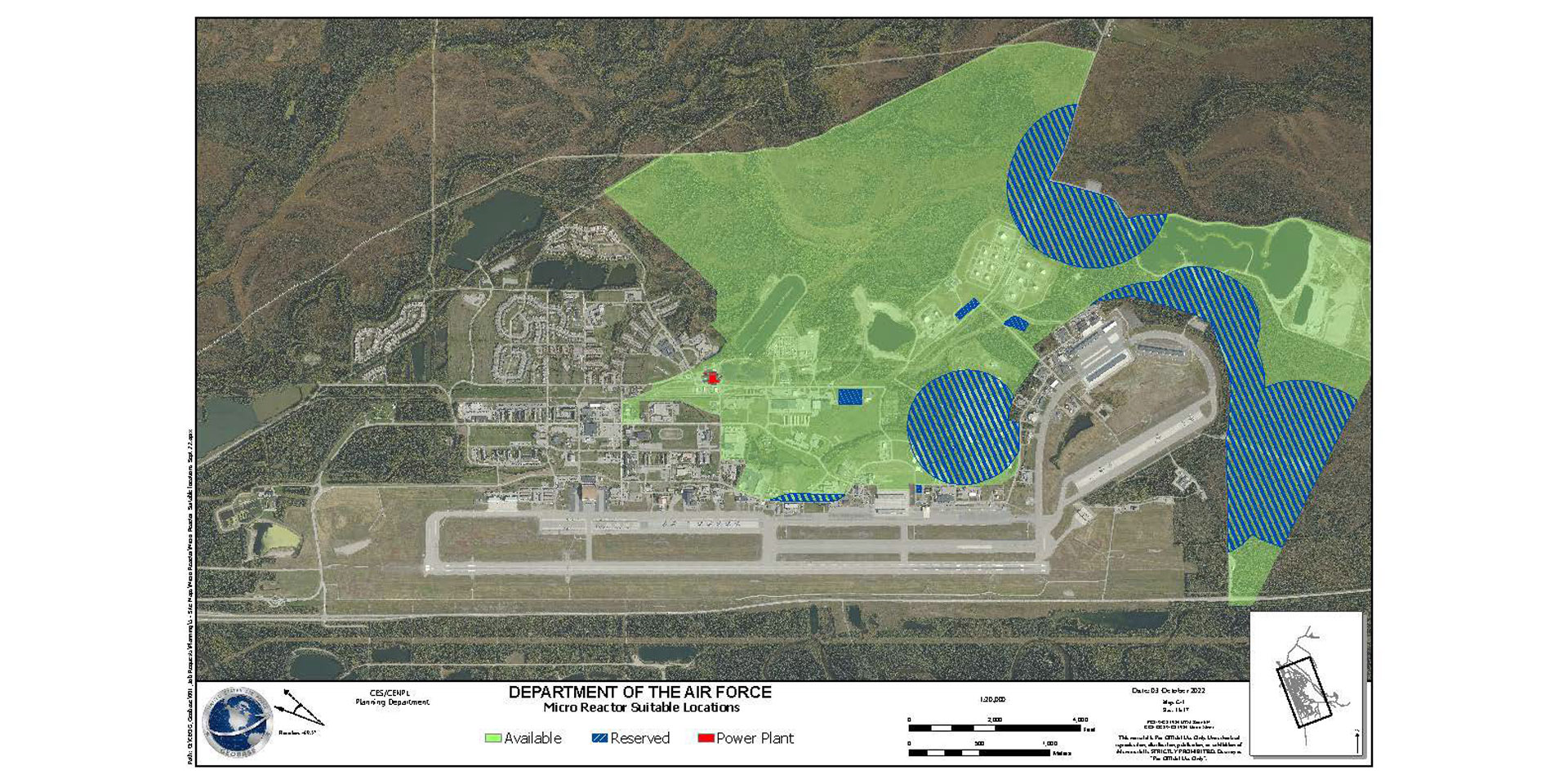
A map of the potential reactor siting area (in green) at Eielson Air Force Base in Alaska provided during a pre-proposal conference in October 2022. (Graphic: Department of the Air Force)
Plans announced with fanfare sometimes falter in the face of competition or economics. Take NuScale Power’s plans for the Carbon Free Power Project in Idaho: The project was canceled in mid-November by NuScale and its first customer, Utah Associated Municipal Power Systems, after nearly a decade. The significance of that news depends on the observer. NuScale intends to focus on other sites and customers. Competitors may redouble efforts to tout their own designs and customer lists. Media found an opportunity to speculate about the future of advanced nuclear. And while many in the nuclear community believe the momentum in favor of new nuclear deployments is continuing—or even increasing as COP28 continues—others would caution against high hopes and point to the persistent obstacles of regulation, supply chain constraints, and financing costs.
Concept art of the six-module CFPP at INL, terminated before construction could begin. (Image: NuScale)
Utah Associated Municipal Power Systems (UAMPS) and NuScale Power announced November 8 that they have mutually agreed to end the Carbon Free Power Project (CFPP)—a plan to build a set of 77-MWe pressurized water reactors, called NuScale Power Modules, at Idaho National Laboratory. The reactors were intended to provide power to INL and UAMPS customers in Utah and surrounding states with an anticipated start date of 2029.
Participating in the forum were (from left) John Hopkins (NuScale Power), Renaud Crassous (EDF), Daniel Poneman (Centrus Energy), Adriana Cristina Serquis (CNEA), and Boris Schucht (Urenco).
The nuclear industry leaders assembled in Washington, D.C., last week to discuss small modular reactor supply chains agreed that lost generation capacity from the expected retirement of hundreds or thousands of coal power plants over the next decade—a cliff, in one panelist’s words—represents an opportunity that developers of SMRs and advanced reactors are competing to meet.
“I think in total 80 projects are ongoing,” said Boris Schucht, panel moderator and chief executive officer of Urenco Group, as he opened the forum. “Of course not all of them will win, and we will discuss today what is needed so that they can be successful.”
From left: U.S. undersecretary of state for arms control and international security Bonnie Jenkins; Japan’s state minister of economy, trade, and industry Fusae Ōta; Ghana’s deputy minister of Energy William Owuraku Aidoo; and U.S. assistant secretary for nuclear energy Kathryn Huff. (Photo: DOE Office of Nuclear Energy)
The United States and Japan have announced Winning an Edge Through Cooperation in Advanced Nuclear (WECAN)—a new agreement aimed at supporting the deployment of small modular reactors and other advanced reactor technologies in partner countries.
Conceptual layout and deployment of a Prodigy SMR Marine Power Station with 12 NuScale Power Modules. (Graphic: Business Wire)
NuScale Power and Prodigy Clean Energy announced on October 26 that they have developed a conceptual design for a transportable, marine-based small modular reactor. The companies plan to present the design to utilities, regulators, and shipyard manufacturers. Prodigy, a Canadian company “specializing in the development of transportable nuclear power plants,” and NuScale signed a memorandum of understanding in 2018 agreeing to pursue the development of an SMR marine facility.
From left: Romanian energy minister Virgil Popescu; E-Infra CEO Teofil Mureșan; Nuclearelectrica board chairman Teodor Chirica; and U.S. undersecretary for economic development, energy, and environment Jose Fernandez. (Photo: Nuclearelectrica)
Energy firms Nuclearelectrica and Nova Power & Gas have launched a joint venture, RoPower Nuclear, for the development of small modular reactors in Romania, with SMR technology provided by NuScale Power, of Portland, Ore.
Largely state-owned, Nuclearelectrica operates Romania’s sole nuclear power facility, the two-unit Cernavoda plant, while Nova Power & Gas, a subsidiary of the privately held E-Infra Group, is a supplier and distributor of electricity and natural gas in Romania. The two firms own equal shares of RoPower.
Members of the Paragon Energy Solutions, Reuter-Stokes, and NuScale Power teams during a recent visit to Reuter-Stokes’ global headquarters in Twinsburg, Ohio. (Photo: Reuter-Stokes)
Paragon Energy Solutions and Reuter-Stokes have signed a contract to design and manufacture neutron monitoring detectors for small modular reactor developer NuScale Power.
An artist's rendering of the NuScale plant. (Image: NuScale Power)
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission has directed its staff to issue a final rule certifying NuScale Power’s small modular reactor design for use in the United States, the agency announced last Friday.
Certification of the Portland, Ore.–based SMR developer’s design will become effective 30 days after publication of the rule in the Federal Register. The design will be incorporated as Appendix G to 10 CFR Part 52, Licenses, Certifications, and Approvals for Nuclear Power Plants.
Rendering of a VOYGR plant. (Image: NuScale)
NuScale Power and Paragon Energy Solutions have signed a patent license agreement that will make NuScale’s Nuclear Regulatory Commission–approved reactor protection system architecture available to the broader nuclear industry, the two companies announced on July 12.
Known as the Highly Integrated Protection System (HIPS) platform, the system was developed by NuScale and Rock Creek Innovations (RCI), a hardware supplier of commercial nuclear protections systems, over six years of collaboration that began in 2010. Paragon, a supplier of safety-related parts and components, acquired RCI in December 2021.
This image is described by the Alaska Center for Energy and Power as a conceptual layout of a generic small modular reactor or microreactor. (Image: ACEP)
Alaska Gov. Mike Dunleavy (R.) introduced “An act relating to microreactors” (SB 177) in the Alaska state legislature on February 1 that would modify existing state law on nuclear energy by specifying that microreactors are not subject to certain nuclear reactor siting and permitting regulations in Alaska. The bill defines a microreactor as an advanced nuclear fission reactor that would be capable of generating no more than 50 MWe.